What Is Free Fatty Acid

Alpha linolenic acid ala is the most common omega 3 fatty acid in your diet.
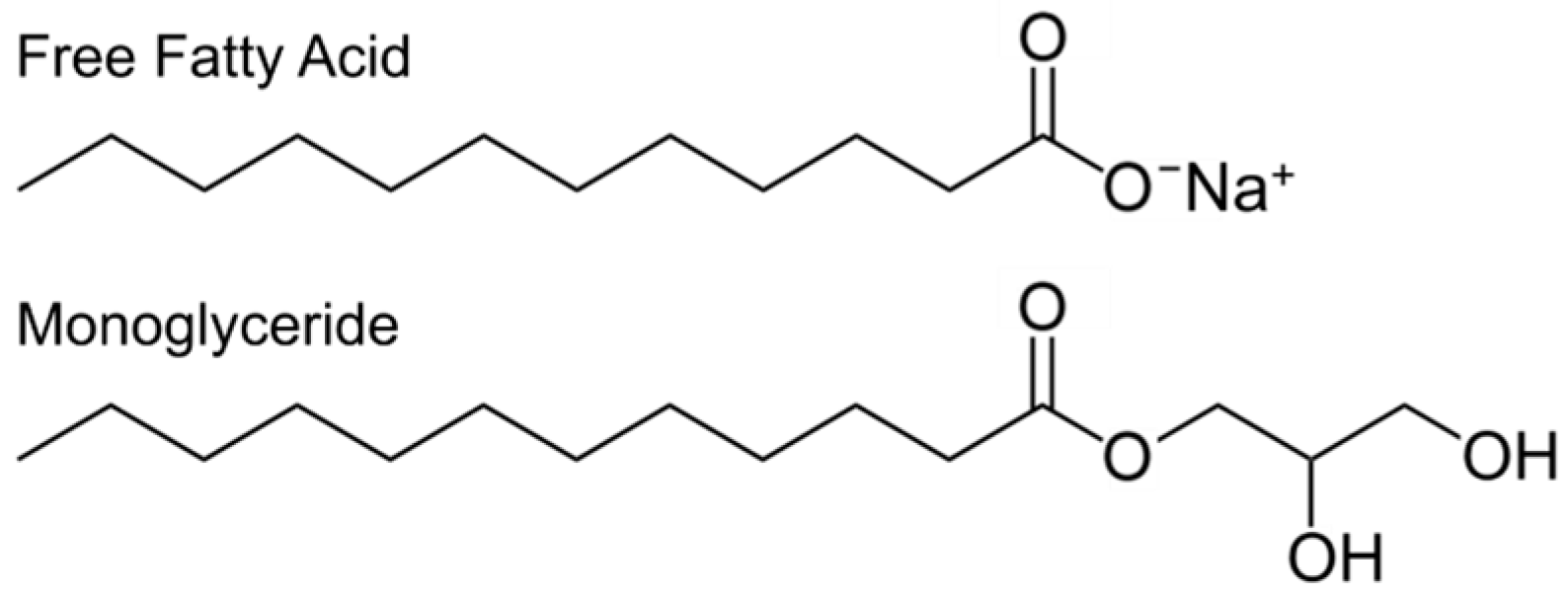
What is free fatty acid. When circulating in the plasma plasma fatty acids not in their ester fatty acids are known as non esterified fatty acids nefas or free fatty acids ffas. Fatty acids that are attached to for. In the plasma the nonesterified fatty acids released immediately combine with albumin to form bound free fatty acids. In the saponification reaction the triglycerides hydrolyze to yield fatty acids that react with the alkali to form soap whereas the free fatty acids directly react with the base while conducting the experiments to find out the acid value.
Ffas are always bound to a transport protein such as albumin. Among the most widely distributed fatty acids are the 16 and 18 carbon fatty acids otherwise known as palmitic acid and stearic acid respectively. In biochemistry ffa free fatty acid is also referred to as nefa non esterified fatty acid because in living things there is more f a. In adipose tissue this is mostly in the form of triglycerides.
Any of a large group of organic acids especially those found in animal and vegetable fats and oils. Fatty acids are mainly composed of long chains of carbon atoms linked to hydrogen atoms. Free fatty acids are those acids that are not present as triglycerides fats in the biodiesel. The metabolism of fatty acids involves the uptake of free fatty acids by cells via fatty acid binding proteins which transport the fatty acids intracellularly from the plasma membrane.
A fatty acid is saturated when the bonds between carbon atoms are all single bonds. Fatty acid s rarely occur as free molecules in nature but are usually found as components of many complex lipid molecules. There are three main types of omega 3 fatty acids ala dha and epa. Your body mainly uses it for energy.
The form in which a fatty acid leaves the cell to be transported for use in another part of the body. These are almost all glycerol esters. Free fatty acids are those long chain acids fatty acids that are not conjugated or attached to anything else.